Blood cells
There are three main types of cells in your blood – red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Different types of blood cancer affect different types of blood cell.
White blood cells
White blood cells help your body fight infection. They are part of your immune system.
The main types of white blood cell are:
- neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils (all called granulocytes)
- lymphocytes (there are B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes)
- monocytes.
Red blood cells
Your red blood cells carry oxygen from your lungs to all the cells in your body. Inside your red blood cells there is a protein called haemoglobin which helps carry the oxygen.
Platelets
Platelets help your blood to clot. They stick together to stop bleeding if you have a cut or a bruise.
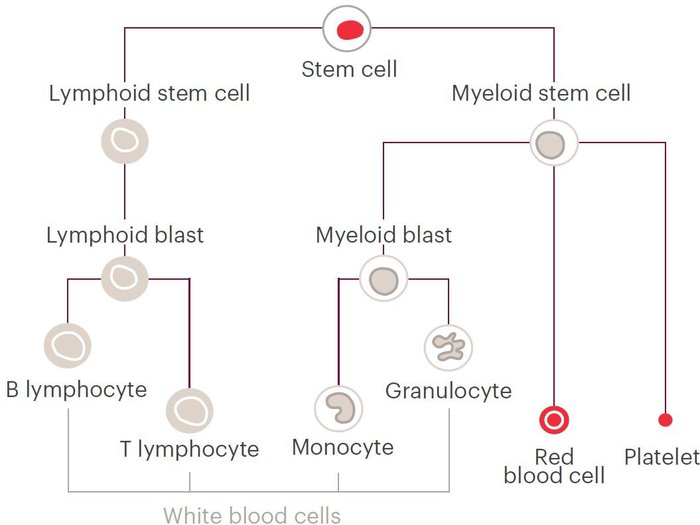
How blood cells normally develop
All your blood cells start off as special cells called blood stem cells, which are made in the bone marrow (a soft material inside your bones).
Blood stem cells can divide and multiply in the bone marrow to produce many other blood cells. The diagram below shows how blood stem cells can grow into any of the blood cells that are needed, including white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets.
Your bone marrow makes a huge number of blood cells every second. If everything’s working normally, your body makes the right number of each type of cell to keep you healthy.
If something goes wrong with the process below, blood cancer can occur, and you may get blood cells not developing properly, or multiplying too quickly.
Blood cells
Full blood count
A full blood count is a blood test that checks the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets in your blood.
Everyone has slightly different numbers of each type of blood cell. If you’re healthy, the amount normally stays the same, with slight changes over time.
Below is an idea of the normal ranges for blood cells in a healthy adult.
The numbers might look complicated, but your health care team may use them in a simple way. For example, ‘your haemoglobin is 140’ or ‘your neutrophils are 4’.
Levels found in a healthy person by cell type
- Haemoglobin (Hb) level - 130-180 g/l (men), 115-165 g/l (women)
- Platelets - 150-400 x 10⁹/l
- White blood cells (WBC) - 4.0-11.0 x 10⁹/l
- Neutrophils - 2.0-7.5 x 10⁹/l
- Lymphocytes - 1.5-4.5 x 10⁹/l

Worried about anything or have questions?
If you need someone to talk to, please don't hesitate to contact our Support Service by phone or email.
