What is Hodgkin lymphoma?
Hodgkin lymphoma is a type of blood cancer that affects blood cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that help to fight infection.
Hodgkin lymphoma explained
If you’ve got Hodgkin lymphoma, some of your lymphocytes become cancerous, which means they multiply in an abnormal way. These cancerous cells cluster together in your glands (lymph nodes), attracting normal white blood cells and causing lumps to form.
Usually, the lumps will be in your neck or chest, but you can get them anywhere you have lymph nodes. Some people also get lumps in other parts of the body.
Lymphocytes and lymph nodes are part of your lymphatic system, so Hodgkin lymphoma is also called a cancer of the lymphatic system.
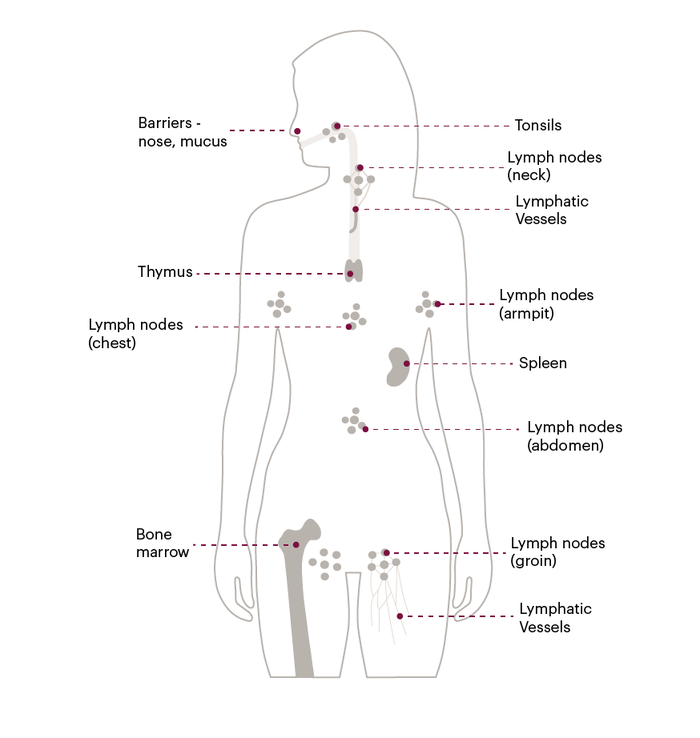
The lymphatic system
Your lymphatic system
The lymphatic system is part of your immune system and has an important role in helping your body to fight infections.
The lymphatic system is made up of a network of thin tubes called lymph vessels that connect small glands called lymph nodes. A fluid called lymph travels through the vessels and nodes. It contains lots of lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell that fights infection).
The lymphatic system also includes the spleen, the tonsils and a small gland in the chest called the thymus.
Hodgkin lymphoma can affect any part of the lymphatic system. Sometimes it can affect other parts of the body, such as the lungs, kidneys and bone marrow, but this is less common.
"It was hard trying to explain it to everybody, because nobody around me knew what it was. People would look it up, see the word cancer and immediately think the worst."
Helen, diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma in 2007.

The difference between Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma
There are two main types of lymphoma: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Both types affect your lymphocytes. But in most forms of Hodgkin lymphoma, the cancerous lymphocytes are called Reed-Sternberg cells. If you have a lymph node biopsy and these cells are found in your sample, you will be diagnosed with classic Hodgkin lymphoma (often called classical Hodgkin lymphoma).
Hodgkin lymphoma is named after the doctor who first recognised it, Thomas Hodgkin.
Types of Hodgkin lymphoma
There are two main types of Hodgkin lymphoma:
- classic Hodgkin lymphoma
- nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL).
Classic Hodgkin lymphoma is the most common type. Around 2,000 people are diagnosed with it each year.
NLPHL is much less common. Around 200 people are diagnosed with it each year. It usually develops more slowly than classic Hodgkin lymphoma and has different treatment.
In our information we focus on classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Lymphoma Action has detailed information about nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL).
Types of classic Hodgkin lymphoma
There are four sub-types of classic Hodgkin lymphoma:
- nodular sclerosis classic Hodgkin lymphoma (this is the most common type)
- mixed cellularity classic Hodgkin lymphoma
- lymphocyte-rich classic Hodgkin lymphoma
- lymphocyte-depleted classic Hodgkin lymphoma.
All the subtypes of classic Hodgkin lymphoma are diagnosed and treated in the same way.
Who gets Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma can happen at any age, but it’s more common in young adults and people over 75. In the UK its slightly more common in people born male than people born female.
Find out more about risk factors and causes of Hodgkin lymphoma.

Your free guide to Hodgkin lymphoma
A booklet to help you understand your diagnosis and treatment, look after yourself and get support.
